The genetic software for Longevity Clinics
The genetic software for Longevity Clinics
The genetic software for Longevity Clinics
Integrate genetics into your dermatology clinic with N-Gene, the software for dermatology professionals that offers personalized solutions to your clients with genetic studies and helps grow your business.
Integrate genetics into your dermatology clinic with N-Gene, the software for dermatology professionals that offers personalized solutions to your clients with genetic studies and helps grow your business.

The most comprehensive
Explore our solutions
Explore the predisposition and protection to:
The most comprehensive
Explore our solutions
Skin properties
Antioxidant Capacity
The protection of the skin against oxidative damage is determined by genes such as SOD2 and GPX1, which are involved in the neutralization of free radicals. Variants in these genes can reduce antioxidant capacity, favoring premature aging and sensitivity to environmental factors such as pollution and UV radiation.
Cellulitis
The accumulation of fat and the structure of connective tissue are regulated by genes such as ACE and HIF1A, which influence microcirculation and collagen distribution. Polymorphisms in these genes may predispose to greater fluid retention and lower skin firmness, favoring the development of cellulite.
Skin elasticity
The firmness and elasticity of the skin depend on the production of collagen and elastin, regulated by genes such as COL1A1 and ELN. Polymorphisms in these genes can influence the structure of connective tissue, affecting the skin's resistance to sagging and wrinkle formation.
Skin hydration
The skin's ability to retain moisture is influenced by genes such as AQP3, which regulates cell hydration. Polymorphisms in this gene can affect water retention, predisposing the skin to be drier or have a lower capacity to protect against external aggressions.
Tendency to tan and sunburns
The skin's response to solar radiation is influenced by variants in MC1R, a key gene in melanin production. Polymorphisms in MC1R can determine a greater sensitivity to sunburn or a better tanning capacity, affecting natural protection against UV radiation.
Varicose veins
The predisposition to chronic venous insufficiency and the formation of varicose veins is influenced by genes such as FOXC2 and COL5A1, which regulate the integrity of blood vessels and the structure of connective tissue. Variants in these genes can affect circulation and venous resistance, increasing the risk of varices.
Skin properties
Antioxidant Capacity
The protection of the skin against oxidative damage is determined by genes such as SOD2 and GPX1, which are involved in the neutralization of free radicals. Variants in these genes can reduce antioxidant capacity, favoring premature aging and sensitivity to environmental factors such as pollution and UV radiation.
Cellulitis
The accumulation of fat and the structure of connective tissue are regulated by genes such as ACE and HIF1A, which influence microcirculation and collagen distribution. Polymorphisms in these genes may predispose to greater fluid retention and lower skin firmness, favoring the development of cellulite.
Skin elasticity
The firmness and elasticity of the skin depend on the production of collagen and elastin, regulated by genes such as COL1A1 and ELN. Polymorphisms in these genes can influence the structure of connective tissue, affecting the skin's resistance to sagging and wrinkle formation.
Skin hydration
The skin's ability to retain moisture is influenced by genes such as AQP3, which regulates cell hydration. Polymorphisms in this gene can affect water retention, predisposing the skin to be drier or have a lower capacity to protect against external aggressions.
Tendency to tan and sunburns
The skin's response to solar radiation is influenced by variants in MC1R, a key gene in melanin production. Polymorphisms in MC1R can determine a greater sensitivity to sunburn or a better tanning capacity, affecting natural protection against UV radiation.
Varicose veins
The predisposition to chronic venous insufficiency and the formation of varicose veins is influenced by genes such as FOXC2 and COL5A1, which regulate the integrity of blood vessels and the structure of connective tissue. Variants in these genes can affect circulation and venous resistance, increasing the risk of varices.
Aging
Aging
Diseases - Circulatory System
Diseases - Circulatory System
Pharmacogenetics in dermatology
Pharmacogenetics in dermatology
Pigmentation disorders
Pigmentation disorders
Skin diseases
Skin diseases
Supplementation for skin and hair
Supplementation for skin and hair
Save time
Save time
Explore genetic data easily
Register your patients
Request kits and pickups
Generate reports in PDF
Receive AI-powered insights
Register your patients
Monitor the progress of your clients' samples efficiently: assign an alias to every sample and track its status instantly
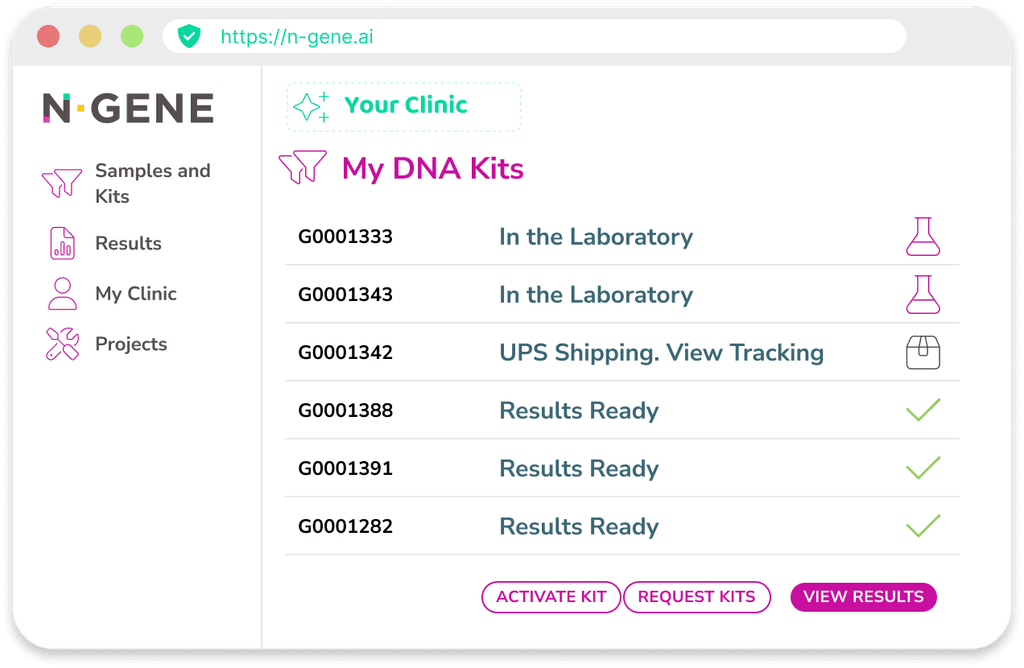
Register your patients
Request kits and pickups
Generate reports in PDF
Receive AI-powered insights

Register your patients
Monitor the progress of your clients' samples efficiently: assign an alias to every sample and track its status instantly
Register your patients
Request kits and pickups
Generate reports in PDF
Receive AI-powered insights

Register your patients
Monitor the progress of your clients' samples efficiently: assign an alias to every sample and track its status instantly
Shall we talk?
Shall we talk?
Shall we talk?
Contact us and request a demo without obligation
Contact us and request a demo without obligation
Contact us and request a demo without obligation
Our experts will provide you with a demonstration of N-GENE and will answer all your questions. Discover all the advantages of integrating genetics into your practice.
Our experts will provide you with a demonstration of N-GENE and will answer all your questions. Discover all the advantages of integrating genetics into your practice.
Contact us via WhatsApp

Do You Need to Know More?
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to be an expert in genetics to interpret the reports?
How do I collect the samples from my patients?
Are the results reliable?
Can this test be used as a diagnosis?
Where do I send the samples and what technology do you use?
Is it necessary to repeat the test after a few months?
How is the privacy of the samples handled?
Discover how N-GENE can transform your medical consultation
Discover how N-GENE can transform your medical consultation
Fundamental today, essential tomorrow
The genetic reports from N-GENE are informative and preventive. They do not constitute a medical diagnosis nor do they substitute for individual clinical assessment.
The genetic reports from N-GENE are informative and preventive. They do not constitute a medical diagnosis nor do they substitute for individual clinical assessment.







