The genetic solution for Gynecologists
The genetic solution for Gynecologists
The genetic solution for Gynecologists
Integrate genetics into your gynecological practice with N-Gene, the software for gynecology and obstetrics professionals that offers personalized solutions to your clients with genetic studies and helps grow your business.
Integrate genetics into your gynecological practice with N-Gene, the software for gynecology and obstetrics professionals that offers personalized solutions to your clients with genetic studies and helps grow your business.



The most comprehensive
Explore our solutions
Multiple variants
Explore the predisposition and protection for:
Intestinal and metabolic health
Caffeine
Tolerance and the effects of caffeine mainly vary due to variants in the gene CYP1A2, responsible for its metabolism in the liver. Polymorphisms like rs762551 determine whether an individual is a fast or slow metabolizer of caffeine, which influences their sensitivity and its impact on sleep, blood pressure, and cognitive performance. Additionally, variants in ADORA2A can modulate the neurological response to caffeine, affecting the propensity to anxiety or tolerance to the stimulant.
Celiac Disease (Gluten)
The genotype HLA-DQ2 and/or HLA-DQ8 is associated with a genetic predisposition to celiac disease, while its absence significantly reduces the likelihood of developing this condition. The identification of these genetic markers allows for the assessment of risk and improves the customization of dietary strategies, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis.
Basal glucose
Fasting glucose levels may be modulated by variants in genes such as TCF7L2 and GCK, which influence the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Polymorphisms in TCF7L2 have been associated with an increased predisposition to insulin resistance and the risk of type 2 diabetes, while variants in GCK may affect the pancreas's sensitivity to glucose levels.
Histamine intolerance
The genotype in variants of the gene AOC1 (DAO) may influence the ability to degrade histamine, which can increase the predisposition to intolerance to this biogenic amine. The variants that reduce the activity of the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO) may favor the accumulation of histamine and trigger adverse symptoms.
Lactose intolerance
The CC genotype at the SNP C/T_13910 indicates a high genetic predisposition to lactose intolerance, while the C/T or T/T genotypes indicate lactase persistence and thus a lower predisposition to this intolerance. Knowing this information allows for a personalization of guidelines and dietary treatments in professional consultation.
Intestinal and metabolic health
Caffeine
Tolerance and the effects of caffeine mainly vary due to variants in the gene CYP1A2, responsible for its metabolism in the liver. Polymorphisms like rs762551 determine whether an individual is a fast or slow metabolizer of caffeine, which influences their sensitivity and its impact on sleep, blood pressure, and cognitive performance. Additionally, variants in ADORA2A can modulate the neurological response to caffeine, affecting the propensity to anxiety or tolerance to the stimulant.
Celiac Disease (Gluten)
The genotype HLA-DQ2 and/or HLA-DQ8 is associated with a genetic predisposition to celiac disease, while its absence significantly reduces the likelihood of developing this condition. The identification of these genetic markers allows for the assessment of risk and improves the customization of dietary strategies, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis.
Basal glucose
Fasting glucose levels may be modulated by variants in genes such as TCF7L2 and GCK, which influence the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Polymorphisms in TCF7L2 have been associated with an increased predisposition to insulin resistance and the risk of type 2 diabetes, while variants in GCK may affect the pancreas's sensitivity to glucose levels.
Histamine intolerance
The genotype in variants of the gene AOC1 (DAO) may influence the ability to degrade histamine, which can increase the predisposition to intolerance to this biogenic amine. The variants that reduce the activity of the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO) may favor the accumulation of histamine and trigger adverse symptoms.
Lactose intolerance
The CC genotype at the SNP C/T_13910 indicates a high genetic predisposition to lactose intolerance, while the C/T or T/T genotypes indicate lactase persistence and thus a lower predisposition to this intolerance. Knowing this information allows for a personalization of guidelines and dietary treatments in professional consultation.
Intestinal and metabolic health
Caffeine
Tolerance and the effects of caffeine mainly vary due to variants in the gene CYP1A2, responsible for its metabolism in the liver. Polymorphisms like rs762551 determine whether an individual is a fast or slow metabolizer of caffeine, which influences their sensitivity and its impact on sleep, blood pressure, and cognitive performance. Additionally, variants in ADORA2A can modulate the neurological response to caffeine, affecting the propensity to anxiety or tolerance to the stimulant.
Celiac Disease (Gluten)
The genotype HLA-DQ2 and/or HLA-DQ8 is associated with a genetic predisposition to celiac disease, while its absence significantly reduces the likelihood of developing this condition. The identification of these genetic markers allows for the assessment of risk and improves the customization of dietary strategies, facilitating a more accurate diagnosis.
Basal glucose
Fasting glucose levels may be modulated by variants in genes such as TCF7L2 and GCK, which influence the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Polymorphisms in TCF7L2 have been associated with an increased predisposition to insulin resistance and the risk of type 2 diabetes, while variants in GCK may affect the pancreas's sensitivity to glucose levels.
Histamine intolerance
The genotype in variants of the gene AOC1 (DAO) may influence the ability to degrade histamine, which can increase the predisposition to intolerance to this biogenic amine. The variants that reduce the activity of the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO) may favor the accumulation of histamine and trigger adverse symptoms.
Lactose intolerance
The CC genotype at the SNP C/T_13910 indicates a high genetic predisposition to lactose intolerance, while the C/T or T/T genotypes indicate lactase persistence and thus a lower predisposition to this intolerance. Knowing this information allows for a personalization of guidelines and dietary treatments in professional consultation.
Oncology
Oncology
Oncology
Autoimmune and bone renal health
Autoimmune and bone renal health
Autoimmune and bone renal health
Cardiovascular health
Cardiovascular health
Cardiovascular health
Endocrine health
Endocrine health
Endocrine health
Vitamins, minerals, and omegas in gynecology
Vitamins, minerals, and omegas in gynecology
Vitamins, minerals, and omegas in gynecology
Save time
Save time
Explore genetic data easily
Register your patients
Request kits and pickups
Generate reports in PDF
Receive AI-powered insights
Register your patients
Monitor the progress of your clients' samples efficiently: assign an alias to every sample and track its status instantly
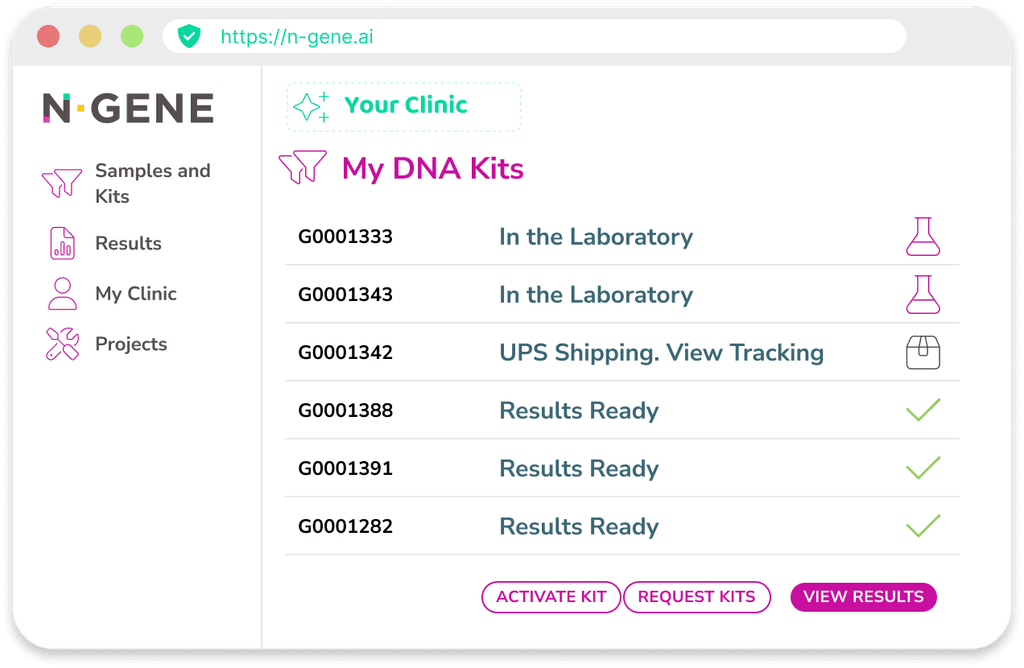
Register your patients
Request kits and pickups
Generate reports in PDF
Receive AI-powered insights

Register your patients
Monitor the progress of your clients' samples efficiently: assign an alias to every sample and track its status instantly
Register your patients
Request kits and pickups
Generate reports in PDF
Receive AI-powered insights

Register your patients
Monitor the progress of your clients' samples efficiently: assign an alias to every sample and track its status instantly
Shall we talk?
Shall we talk?
Shall we talk?
Contact and request a demo without obligation
Contact and request a demo without obligation
Contact and request a demo without obligation
Our experts will provide you with a demonstration of N-GENE and answer all your questions. Discover all the advantages of integrating genetics into your practice.
Our experts will provide you with a demonstration of N-GENE and answer all your questions. Discover all the advantages of integrating genetics into your practice.
Our experts will provide you with a demonstration of N-GENE and answer all your questions. Discover all the advantages of integrating genetics into your practice.
Contact us via WhatsApp

The most comprehensive
Explore our solutions
Do You Need to Know More?
Frequently Asked Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to be an expert in genetics to interpret the reports?
Do I need to be an expert in genetics to interpret the reports?
Do I need to be an expert in genetics to interpret the reports?
How do I collect the samples from my patients?
How do I collect the samples from my patients?
How do I collect the samples from my patients?
Are the results reliable?
Are the results reliable?
Are the results reliable?
Can this test be used as a diagnosis?
Can this test be used as a diagnosis?
Can this test be used as a diagnosis?
Where do I send the samples and what technology do you use?
Where do I send the samples and what technology do you use?
Where do I send the samples and what technology do you use?
Is it necessary to repeat the test after a few months?
Is it necessary to repeat the test after a few months?
Is it necessary to repeat the test after a few months?
How is the privacy of the samples handled?
How is the privacy of the samples handled?
How is the privacy of the samples handled?
Discover how N-GENE can transform your medical consultation
Discover how N-GENE can transform your medical consultation
Fundamental today, essential tomorrow
The genetic reports from N-GENE are informative and preventive. They do not constitute a medical diagnosis nor do they substitute for individual clinical assessment.
The genetic reports from N-GENE are informative and preventive. They do not constitute a medical diagnosis nor do they substitute for individual clinical assessment.
The genetic reports from N-GENE are informative and preventive. They do not constitute a medical diagnosis nor do they substitute for individual clinical assessment.







